Medical Device Registration in Japan Overview
Japan is the second biggest market for Medical devices and is expected to reach US $74.4 billion by 2025. Key factors driving growth for medical device registration in Japan are:
- Population increasingly skewed toward geriatrics
- Increase in life-style diseases and chronic health conditions
- A wider population base being covered under universal health insurance
- Regulatory changes to facilitate innovative technologies
Though the market looks promising, the major barrier in obtaining medical device approval in Japan market is the stringent Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) regulations that companies must abide by. To manage their product registrations and liaise with Japan’s regulatory authorities, all foreign medical device and pharmaceutical companies selling in Japan must assign a Japan DMAH agent.
Regulatory Authority: Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) working under the Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare (MHLW)
Regulation: Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act (PMD Act)
Regulatory Pathway: Pre-Market Submission or Pre-Market Certification or Pre-Market Approval
Authorized Representative: MAH/D-MAH
QMS Requirement: Ordinance No. 169, MDSAP Certification
Assessment of Technical Data: Third party for Class II devices and PMDA for Class III and IV devices
Validity of License: Unlimited
Labeling Requirements: PMD Act
Submission Format: Paper
Language: Japanese
Japan Medical Device Classification
Japan has a clear-cut device classification system. The devices are classified into 4 classes based on the risk associated with the device. The registration procedure, document requirements, Technical assessment varies with the class of the device.
|
Device Class |
Risk |
|
Class I |
Low Risk |
|
Class II |
Low/Medium Risk |
|
Class III |
Medium/High Risk |
|
Class IV |
High Risk |
Market Authorization Holder (MAH)
Japan DMAH AgentForeign manufacturers should appoint a Market Authorization Holder (MAH) / Japan DMAH agent as a pre-requisite to market devices in Japan. However, the PMDA allows to appoint a Designated Market Authorization Holder (D-MAH). In the former case, MAH owns and controls the registration and certificate/approval of the product. In the latter case, Foreign manufacturer owns and controls the registration and certificate/approval of product and D-MAH acts as a representative in Japan. It is ideal to appoint a D-MAH rather than MAH as the process to change a D-MAH is easier than changing the MAH.
Foreign Manufacturer Registration (FMR)
All the foreign manufacturing companies which intend to export their devices into Japan must register themselves with the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW). This registration procedure is called as Foreign Manufacturer Registration (FMR), which formerly was known as “Foreign Manufacturer Accreditation (FMA)” or “Accreditation of Foreign Manufacturers (AFM)”.
Japan Medical Device Registration
The registration pathway in Japan depends on various factors such as class of device, assigned JMDN, availability of predicate device and availability of associated Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS). Various registration pathways in Japan are detailed below -
- Pre-market Submission (Todokede): It applies togeneral Medical Devices (Class I), wherein manufacturers can file a pre-market submission to the PMDA. This is a notification, and no review/assessment by the PMDA will be conducted.
- Pre-market Certification (Ninsho):It applies to Class II (and a limited number of Class III) devices, which have an associated certification standard (JIS), and which are subject to pre-market certification. The process is like the European CE Marking process, where reviews are outsourced to a third party like a Notified Body.
- Pre-market Approval (Shonin): SomeClass II and III devices with no specific certification standard and all Class IV devices are subject to the pre-market approval process, also known as Shonin. This application has to be submitted to the PMDA and ultimately obtain approval from the MHLW.
Process flow
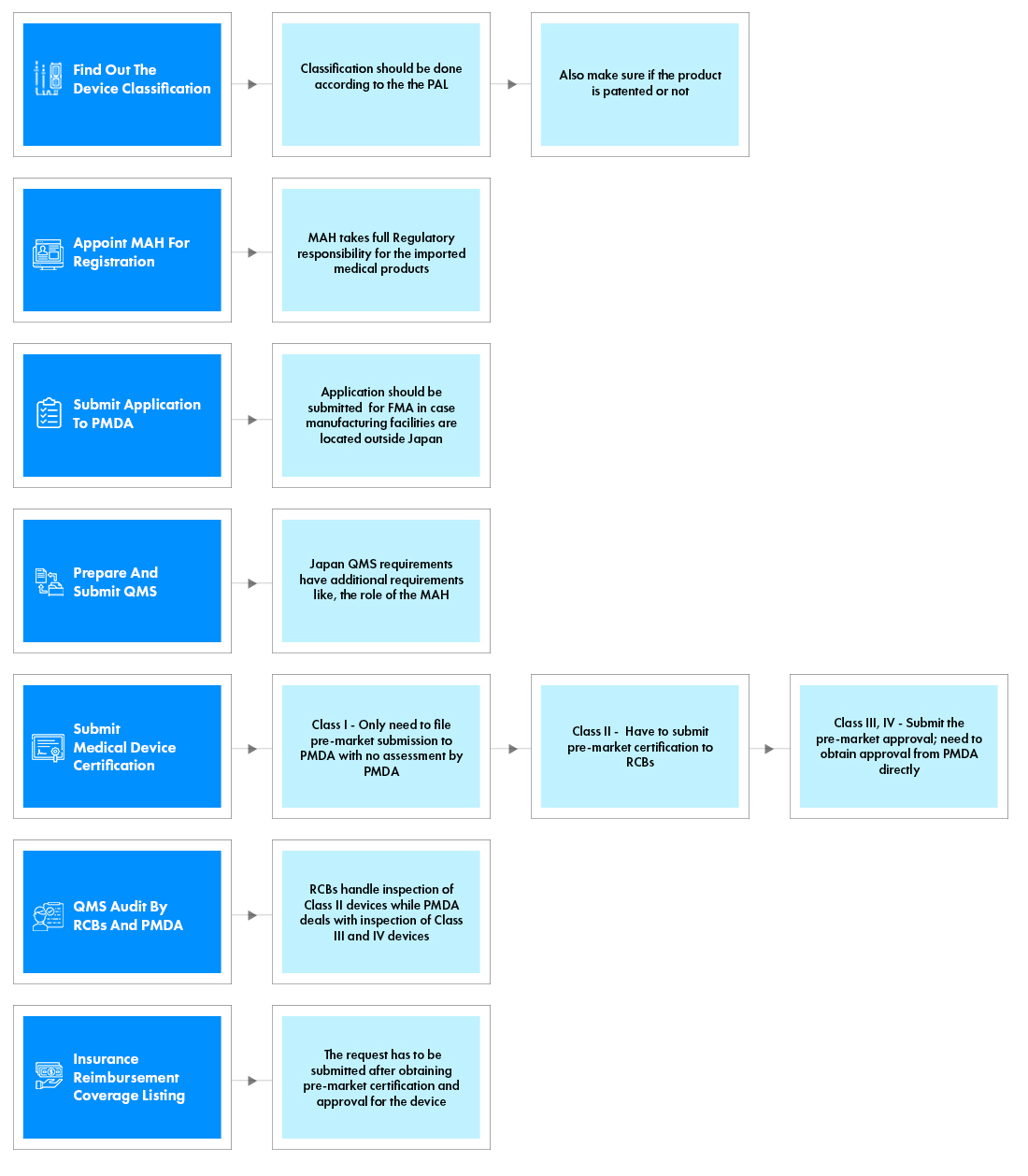
Post Approval Medical Device Life Cycle Management
Freyr supports the foreign manufacturers in end-to-end Medical Device lifecycle management, including post approval activities, such as:
- Post approval change management - modifications to existing Medical Device approvals such as, addition of new variants, accessories; addition of new indications of use among others
- Maintenance of approvals and registration through timely payment of administrative and registration fees
- Renewal of licenses
- Liaising between Notified Body or PMDA and the manufacturer
- Importation Management
Despite having an established medical device Regulatory framework, navigating through Japan’s device classification system and respective registration procedures may require proven expertise.
Freyr, as a strategic Regulatory partner, provides end-to-end Medical Device Regulatory services that span across quality control, classification, clinical safety, and market access. We assist clients in all the procedural challenges right from Regulatory intelligence to dossier preparation and submission to product registration.
Summary
|
Controls |
Device Class |
Risk / Classification Criteria |
Approval Routes |
Agency |
Timelines |
|
General |
Class I |
Low Risk |
Pre-Market Submission (Todokede) |
NA |
1 Month |
|
Specified Controlled |
Class II |
Low/Medium Risk |
Pre-Market Certification (PMC / Ninsho) |
Notified Body |
3-5 months |
|
Controlled |
Class II |
Medium Risk |
Pre-Market Approvals (PMA / Shonin) |
PMDA |
7-9 Months |
|
Highly Controlled |
Class III |
Medium / High Risk |
Pre-Market Approvals (PMA / Shonin) |
PMDA |
9 - 12 Months |
|
Highly Controlled |
Class IV |
High Risk |
Pre-Market Approvals (PMA / Shonin) |
PMDA |
13-16 Months |
Freyr Expertise
- Regulatory Due Diligence
- Device Registration
- Submission Management to PMDA or notified bodies
- MAH and D-MAH
- Pre-Submission Clinical Trial Necessity (CTN) consultation
- Foreign Manufacturer Registration (FMR)
- Data reliability inspection
- QMS inspection
- Reimbursement Application Submission
- Labeling support
- Translation support
- Distributor identification and qualification